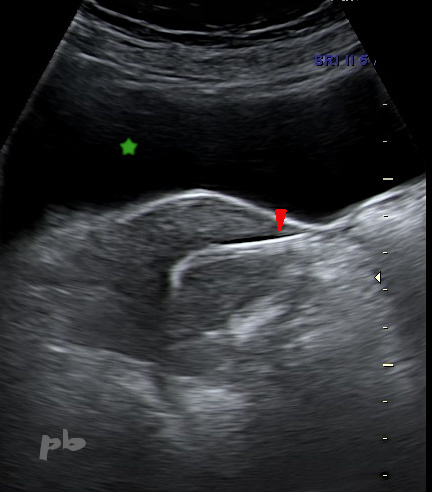
26 – Essure
Echographie par voie sus-pubienne. Coupe transversale.
Système Essure en situation cavitaire et tubaire interstitielle (►) du côté gauche. Il apparait très hyperéchogène du fait sa position, perpendiculaire au faisceau d’ultrasons.
Vessie (★).
26 – Essure
Suprapubic ultrasound. Transverse section.
Essure system in cavitary and interstitial tubal position (►) on the left side. It appears highly echogenic due to its position, perpendicular to the ultrasound beam.
Bladder (★).
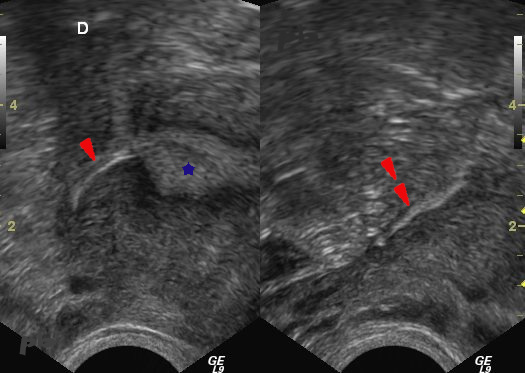
27 – Essure
Echographie endo-vaginale.
L’implant droit est d’abord imagé dans le segment interstitiel de la trompe (►), puis dans la portion proximale du segment isthmique (►►).
Endomètre et cavité utérine (★)
27 – Essure
Transvaginal ultrasound.
The right implant is first visualized in the interstitial segment of the tube (►), then in the proximal portion of the isthmic segment (►►).
Endometrium and uterine cavity (★).
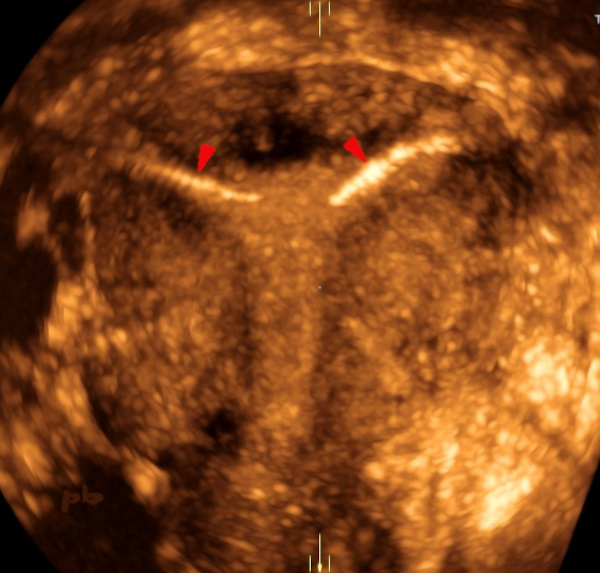
28 – Essure
Echographie endovaginale – Acquisition 3D et reconstruction frontale.
Les implants sont bien en place, avec une portion intra-cavitaire et la partie distale intra-tubaire (segment interstitiel ►).
28 – Essure
Transvaginal ultrasound – 3D acquisition and frontal reconstruction.
The implants are correctly positioned, with an intra-cavitary portion and the distal intra-tubal part (interstitial segment ►).
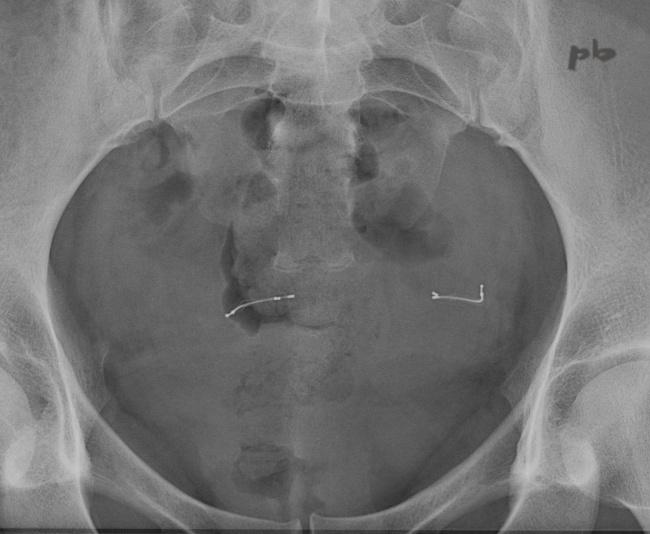
29 – Essure
ASP.
Aspect radiologique normal.
29 – Essure
Abdominal X-ray.
Normal radiographic appearance.
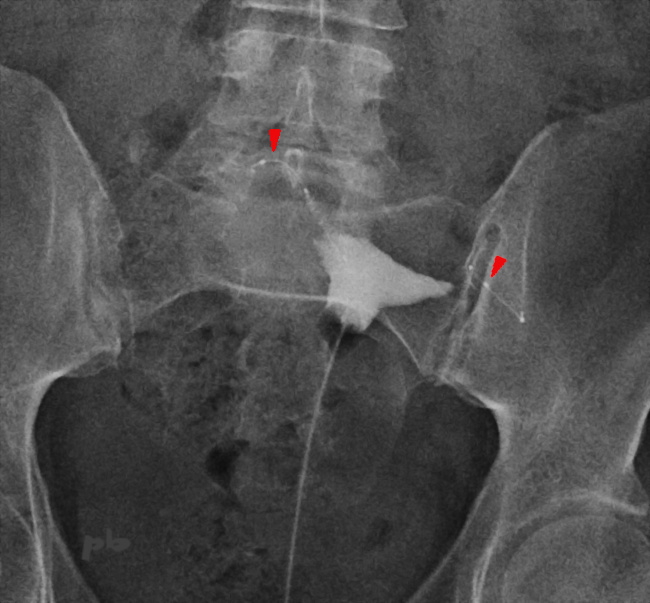
30 – Essure
Hystérosalpingographie (HSG) réalisée après la pose d’un système Essure (►) pour vérifier l’absence de passage tubaire et donc l’efficacité de la stérilisation.
30 – Essure
Hysterosalpingography performed after the placement of an Essure system (►) to confirm the absence of tubal patency and thus the effectiveness of sterilization.
© Dr Philippe BASSNAGEL – 2024
