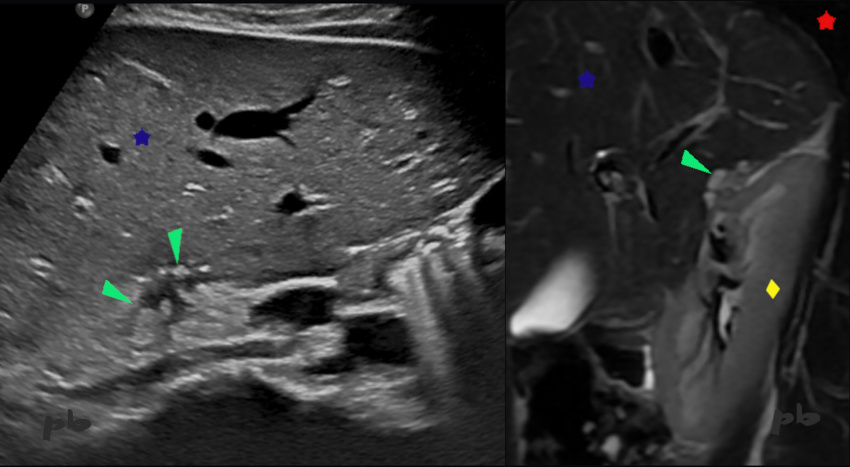
8 – Endométriose diaphragmatique et de l’espace de Morison
Echographie à gauche.
IRM coupe sagittale T2 à droite.
Douleurs cycliques de l’épaule droite. Douleurs pelviennes. Pas de traitement hormonal.
Présence de plusieurs plages de signal intermédiaire en T2 au niveau de l’espace de Morison (►) : implants hémorragiques.
En échographie, il existe une zone hétérogène avec composante kystique et ponctuations hyperéchogènes (►). L’échographie a été réalisée après l’IRM.
Poumon = ★
Foie = ★
Rein droit = ♦
8 – Diaphragmatic endometriosis and Morison’s pouch involvement
Ultrasound on the left. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI on the right.
Cyclic right shoulder pain. Pelvic pain. No hormonal treatment. Presence of multiple intermediate T2 signal areas in Morison’s pouch (►) : hemorrhagic implants. On ultrasound, there is a heterogeneous area with a cystic component and hyperechoic punctuations (►). The ultrasound was performed after the MRI.
Lung (★) – Liver (★ ) – Right kidney (♦)
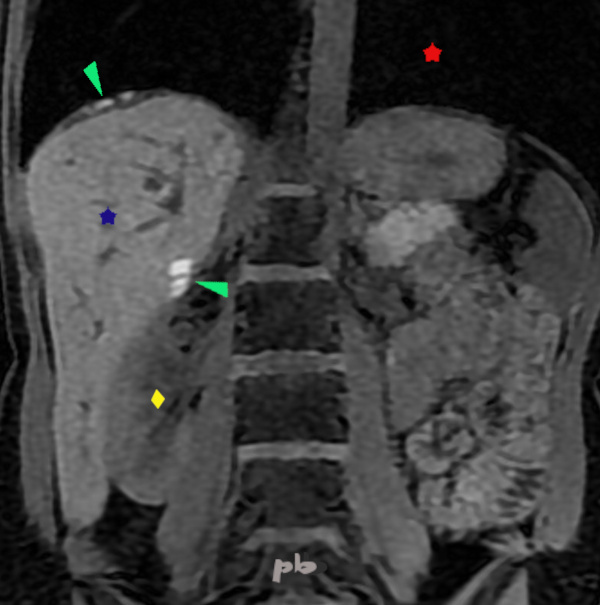
9 – Endométriose diaphragmatique et de l’espace de Morison
(même patiente que 8)
IRM coupe frontale T1
Douleurs cycliques de l’épaule droite.
Présence de plusieurs plages en hypersignal T1 au niveau de l’espace de Morison et de la coupole diaphragmatique droite (►) : implants hémorragiques.
Poumon = ★
Foie = ★
Rein droit = ♦
9 – Diaphragmatic endometriosis and Morison’s pouch involvement
(Same patient as 8)
Frontal T1-weighted MRI. Cyclic right shoulder pain. Pelvic pain. Presence of multiple T1 hyperintense areas in Morison’s pouch and the right diaphragmatic dome (►) : hemorrhagic implants.
Lung (★) – Liver (★ ) – Right kidney (♦)
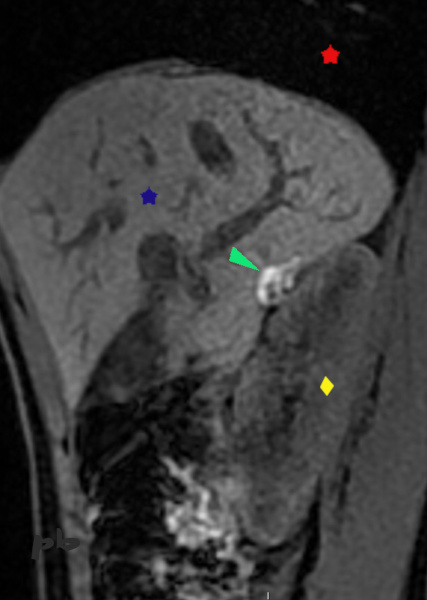
10 – Endométriose diaphragmatique et de l’espace de Morison
(même patiente que 8)
IRM coupe sagittale T1
On retrouve la plage en hypersignal T1 au niveau de l’espace de Morison, correspondant à des lésions endométriosiques.
Poumon = ★
Foie = ★
Rein droit = ♦
10 – Diaphragmatic endometriosis and Morison’s pouch involvement
(Same patient as 8)
Sagittal T1-weighted MRI.
The T1 hyperintense area in Morison’s pouch is visible, consistent with endometriotic lesions.
Lung (★)
Liver = (★ )
Right kidney = (♦)
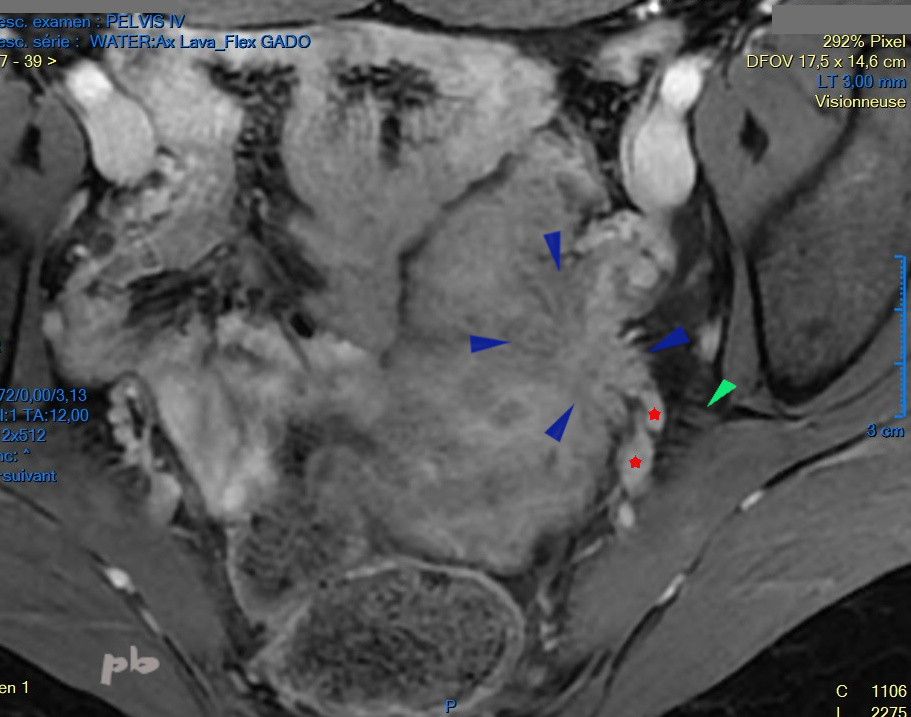
11 – Endométriose urétérale – IRM
IRM coupe axiale fastsat après injection de gadolinium.
Découverte récente d’une urétéro-hydronéphrose gauche sur localisation endométriosique. La patiente se plaint par ailleurs de sciatalgies cycliques.
Volumineux nodule spiculé endométriosique (►), proche de la paroi pelvienne et du nerf grand sciatique (►). Même si le nerf n’apparait pas directement atteint, le nodule est très probablement en rapport avec la symptomatologie douloureuse.
Dans les suites, chirurgie (réimplantation de l’uretère gauche), et traitement médical (pilule en continu). Disparition progressive de la douleur et régression du nodule sur les IRM de contrôle.
Vaisseaux hypogastriques et branches terminales antérieures (★)
11 – Ureteral endometriosis – MRI Axial fat-saturated MRI after gadolinium injection.
Recent discovery of left ureterohydronephrosis due to endometriotic involvement. The patient also reports cyclic sciatica.
Large spiculated endometriotic nodule (►), located near the pelvic wall and the sciatic nerve (►). Although the nerve does not appear directly affected, the nodule is highly likely related to the painful symptoms. Subsequent management included surgical intervention (left ureteral reimplantation) and medical treatment (continuous oral contraceptive pill). Gradual resolution of pain and regression of the nodule on follow-up MRI.
Hypogastric vessels and anterior terminal branches (★)
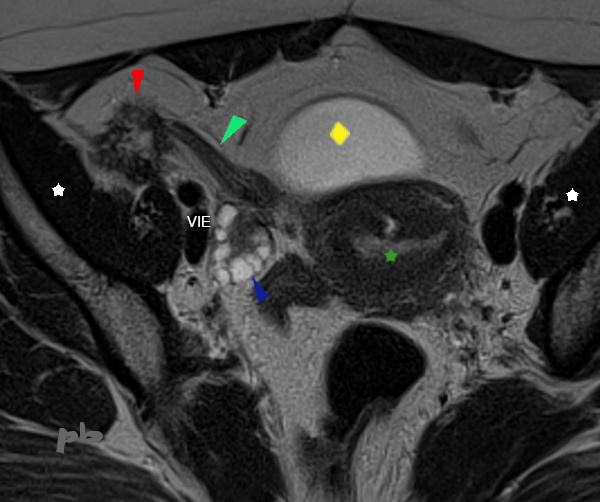
12 – Endométriose du ligament rond
Patiente porteuse d’une endométriose pelvienne profonde avec atteinte rectale. Sous pilule en continu.
IRM coupe axiale T2.
Nodule spiculé (►) en fosse iliaque droite, fixé sur un ligament rond épaissi (►).
Le nodule en-dehors se fixe également à la paroi pelvienne, sur le péritoine et le fascia recouvrant le muscle iliaque (étoile blanche).
Utérus ★
Ovaire droit ►
Vessie ♦
VIE = vaisseaux iliaques externes
12 – Endometriosis of the round ligament Patient with deep pelvic endometriosis involving the rectum. Currently on continuous oral contraceptive pill. Axial T2-weighted MRI.
Spiculated nodule (►) in the right iliac fossa, fixed to a thickened round ligament (►). The nodule also attaches to the pelvic wall, involving the peritoneum and the fascia covering the iliac muscle (white star).
Uterus ★ – Right ovary ► – Bladder ♦ – VIE = external iliac vessels
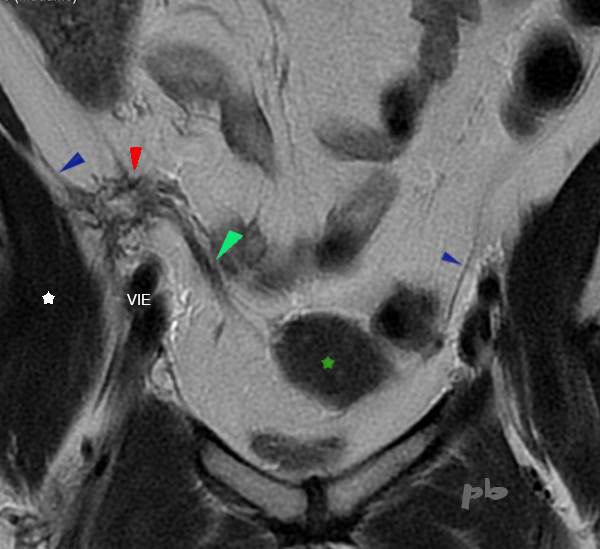
13 – Endométriose du ligament rond
(même patiente que 12)
IRM coupe frontale T2.
Nodule spiculé (►) en fosse iliaque droite, fixé sur le ligament rond (►).
On voit bien la fixation à la paroi pelvienne droite, sur le péritoine et le fascia iliaque, nettement épaissis par rapport au côté gauche (►).
Utérus ★
Muscle iliaque (étoile blanche)
VIE = vaisseaux iliaques externes
13 – Endometriosis of the round ligament
(Same patient as 12) Frontal T2-weighted MRI. Spiculated nodule (►) in the right iliac fossa, fixed to the round ligament (►). Clear attachment to the right pelvic wall, involving the thickened peritoneum and iliac fascia, compared to the left side (►).
Uterus ★ – Iliac muscle (white star) – VIE = external iliac vessels

14 – Endométriose du ligament rond
(même patiente que 12)
IRM coupe frontale T2.
Nodule spiculé (►) en fosse iliaque droite. Sur cette coupe, présence d’adhérences (►) avec le fond du caecum (★).
Vessie ♦
Muscle iliaque (étoile blanche)
Ce nodule endométriosique droit est donc fixé au ligament rond, au péritoine et au fascia du muscle iliaque, ainsi qu’au bas-fond caecal.
14 – Endometriosis of the round ligament
(Same patient as 12)
Frontal T2-weighted MRI.
Spiculated nodule (►) in the right iliac fossa. This slice shows adhesions (►) involving the base of the cecum (★).
Bladder (♦) – Iliac muscle (white star)
This right endometriotic nodule is therefore fixed to the round ligament, peritoneum, iliac muscle fascia, and the cecal base.
© Dr Philippe BASSNAGEL – 2024
