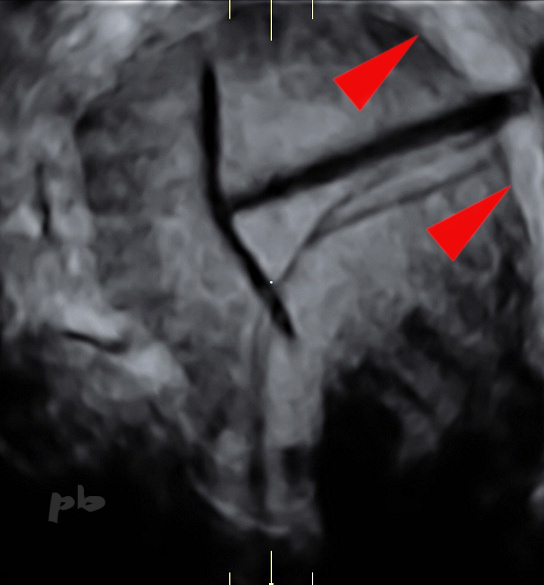
12 – DIU – Artefact
Reconstruction dans le plan frontal de la cavité utérine, du DIU et de ses fils, particulièrement bien visibles.
Le stérilet est basculé, et son extrémité inférieure, gauche perfore la paroi et atteint l’espace péri-utérin.
Contours utérins (►).
12 – IUD – Artifact
Frontal plane reconstruction of the uterine cavity, the IUD, and its strings, which are particularly well visible.
The IUD is tilted, and its lower end, on the left , perforates the uterine wall, reaching the periuterine space.
Uterine contours (►).
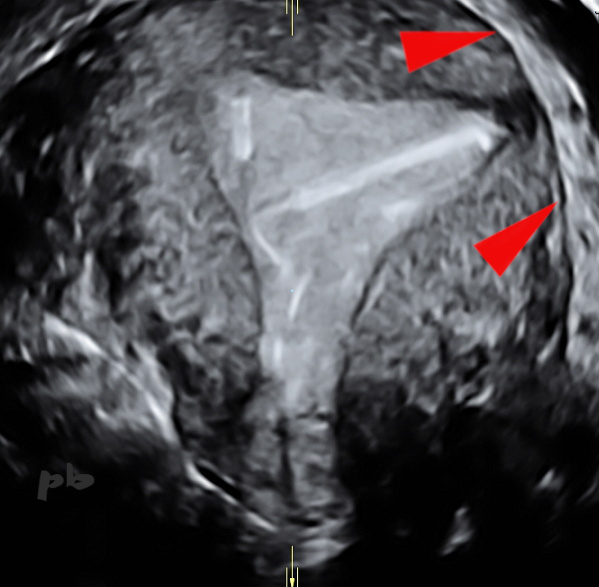
13 -DIU – Artefact
(même patiente que 12)
Reconstruction dans le plan frontal de la cavité utérine, du DIU et de ses fils. Il s’agit de la même patiente et même acquisition volumique que l’image précédente.
Sauf que l’extrémité inférieure du stérilet ne perfore plus la paroi et se situe dans la corne utérine gauche. Le stérilet est certes basculé, mais il est en réalité totalement dans la cavité utérine.
Il s’agit d’un piège classique en 3D : on a reconstruit sur l’image précédente l’ombre du DIU et non le DIU lui-même.
Contours utérins (►).
13 – IUD – Artifact
(same patient as image 12)
Frontal plane reconstruction of the uterine cavity, the IUD, and its strings. This is the same patient and the same volumetric acquisition as the previous image.
However, the lower end of the IUD no longer perforates the uterine wall and is located within the left uterine horn. While the IUD is tilted, it is actually entirely within the uterine cavity.
This is a classic 3D pitfall : in the previous image, the shadow of the IUD was reconstructed, not the IUD itself.
Uterine contours (►).
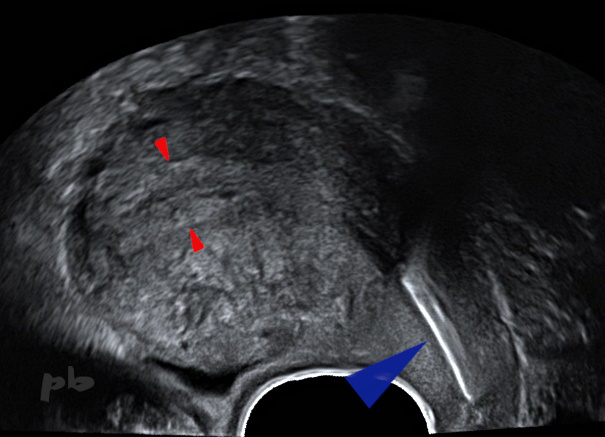
14 – DIU bas situé
Echo endo-vaginale – Coupe sagittale.
Utérus rétroféchi.
DIU (cuivre ►) en situation intra-cervicale.
Endomètre et cavité utérine (►).
14 – Low-positioned IUD
Transvaginal ultrasound – Sagittal view.
Retroflexed uterus.
IUD (copper ►) located within the cervical canal.
Endometrium and uterine cavity (►).

15 – Perforation
HSG réalisée après 2 échecs de pose de DIU.
Le DIU est en position cervico-isthmique. Ses 2 branches latérales situées en-dehors de la lumière utérine, perforent le myomètre (►).
15 – Perforation
HSG performed after 2 failed IUD insertions. The IUD is in a cervico-isthmic position. Its two lateral arms, located outside the uterine lumen, perforate the myometrium (►)
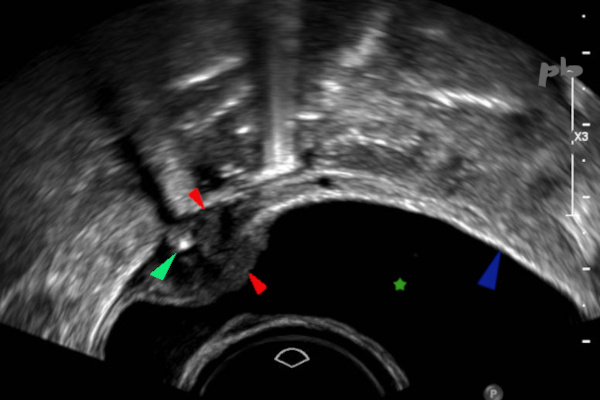
16 – DIU extra-utérin
Echo endo-vaginale.
Examen réalisé avant IVG.
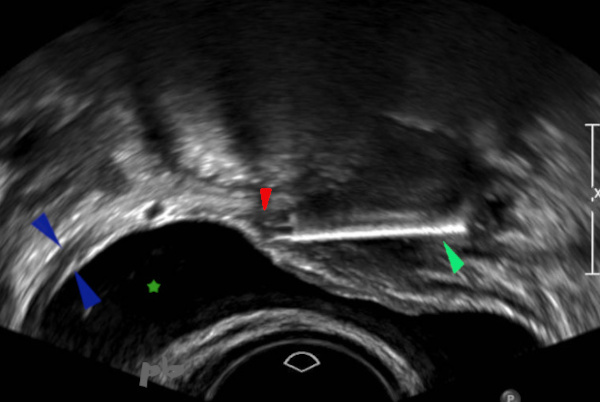
Outre un sac gestationnel intra-utérin, on retrouve un DIU (coupe transversale ►) au niveau du dôme vésical. Il est planté dans la paroi vésicale, avec important œdème, hypoéchogène, en périphérie (►).
Paroi vésicale normale (►).
Vessie (★).
16 – Extrauterine IUD
Transvaginal ultrasound. Examination performed before medical abortion.
In addition to an intrauterine gestational sac, an IUD (cross-sectional view ►) is found at the level of the bladder dome. It is embedded in the bladder wall, with significant surrounding hypoechoic edema (►).
Normal bladder wall (►). Bladder (★).
17 – DIU extra-utérin
(même patiente que 16)
Echo endo-vaginale.
Examen réalisé avant IVG.
Le DIU est cette fois visualisé en coupe longitudinale (►) au niveau du dôme vésical. Sa partie antérieure (►) est extra-vésicale, avec toujours un œdème hypoéchogène en périphérie (►).
Paroi vésicale normale (►). Vessie (★).
17 – Ectopic IUD
(Same patient as 16)
Transvaginal ultrasound. Exam performed before abortion procedure. The IUD is now visualized in longitudinal section (►) at the level of the bladder dome. Its anterior portion (►) is extravesical, with persistent hypoechoic edema peripherally (►).
Normal bladder wall (►).
Bladder (★).
18 – DIU extra-utérin
IRM coupe sagittale T2.
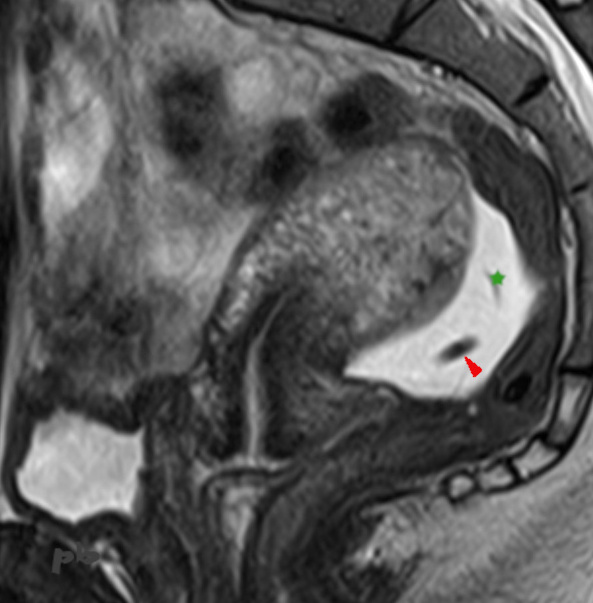
L’examen est demandé pour localisation du stérilet (Mirena) avant coelioscopie et retrait. Il n’était pas retrouvé à l’échographie, mais bien visible dans le pelvis sur l’ASP.
Le DIU (►) est en hyposignal T2 dans le Douglas entouré d’un petit épanchement (★).
Utérus rétrofléchi en avant.
18 – Ectopic IUD – MRI
Sagittal T2-weighted MRI. The exam was requested to locate the IUD (Mirena) before laparoscopy and removal. It was not found on ultrasound but was clearly visible in the pelvis on the abdominal X-ray.
The IUD (►) appears as a T2 hypointense signal in the Douglas pouch, surrounded by a small effusion (★).
Anteriorly retroflexed uterus.
19 – DIU extra-utérin
(même patiente que 18)
IRM coupe sagittale T2.
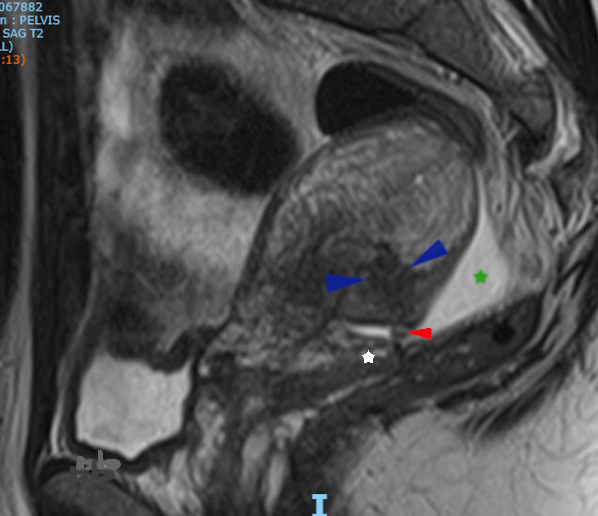
Plus latéralement, le DIU (►) apparait coupé transversalement, en hyposignal T2, entouré de liquide en avant et en arrière (★).
Utérus rétrofléchi en avant. Une plage plus ou moins linéaire et mal délimitée au niveau du myomètre postérieur (►), rejoignant le stérilet, compatible avec son trajet de migration.
Douglas et épanchement (★).
Cul de sac vaginal postérieur (étoile blanche).
19 – Ectopic IUD (Same patient as 18)
Sagittal T2-weighted MRI. More laterally, the IUD (►) appears in cross-section as a T2 hypointense signal, surrounded by fluid anteriorly and posteriorly (★). Retroflexed uterus tilted forward. A more or less linear, poorly defined area in the posterior myometrium (►), connecting to the IUD, consistent with its migration path.
Douglas pouch and effusion (★).
Posterior vaginal fornix (white star).
20 – DIU extra-utérin
Echo endo-vaginale.
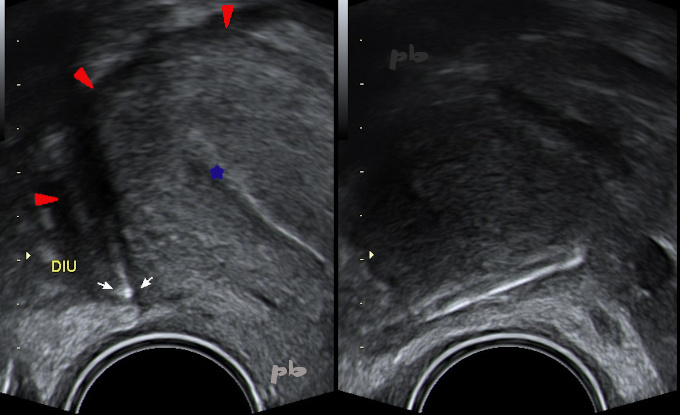
Le stérilet (flèches blanches) est retrouvé dans le Douglas, en coupe transversale (image gauche), et en coupe longitudinale (image droite).
Fond utérin (►).
Endomètre (★).
20 – Ectopic IUD
Transvaginal ultrasound. The IUD (white arrows) is located in the Douglas pouch, shown in transverse section (left image) and longitudinal section (right image).
Uterine fundus (►). Endometrium (★).
© Dr Philippe BASSNAGEL – 2022
