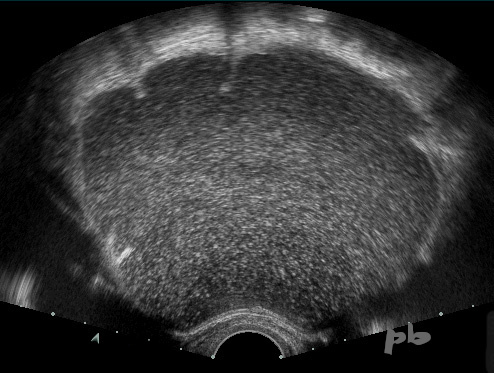
12 – Diagnostic différentiel – Cystadénome mucineux
En échographie, le liquide intra-kystique apparait moins homogène, plus particulaire qu’un kyste endométriosique.
Ce cystadénome mucineux était uniloculaire, renforçant la confusion.
12 – Differential Diagnosis – Mucinous Cystadenoma
In ultrasound, the intra-cystic fluid appears less homogeneous, more particulate than an endometriotic cyst.
This mucinous cystadenoma was unilocular, reinforcing the confusion.
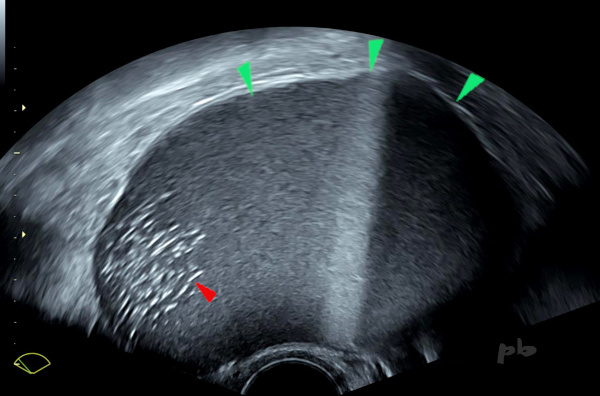
13 – Diagnostic différentiel – Kyste dermoïde
Echographie
On retrouve plusieurs niveaux liquide-liquide (►), plus rarement observés dans les kystes dermoïdes par rapport aux kystes endométriosiques.
En déclive, visualisation d’échos intenses (►) très évocateurs de l’origine dermoïde.
L’IRM a facilement confirmé le diagnostic.
13 – Differential Diagnosis – Dermoid Cyst
Ultrasound
Multiple liquid-liquid levels are found (►), which are less commonly observed in dermoid cysts compared to endometriotic cysts.
In the dependent portion, visualization of intense echoes (►) highly suggestive of a dermoid origin.
MRI easily confirmed the diagnosis.
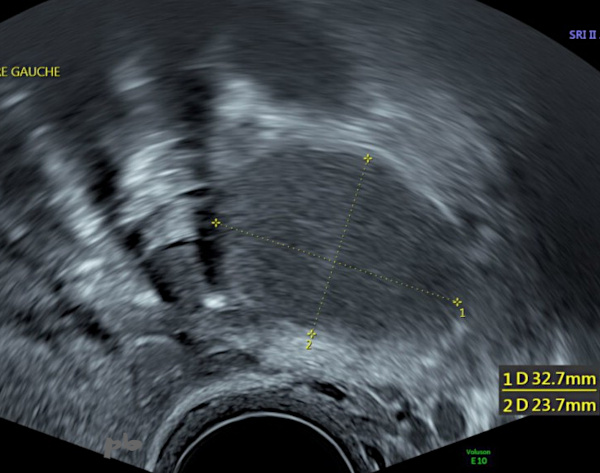
14- Diagnostic différentiel – Corps jaune kystique
Image hypoéchogène homogène et régulière.
Persistance sur 2 échographies de suivi sur une période de 9 mois : faux diagnostic d’endométriome.
Pas d’IRM.
Anapath : corps jaune kystique.
14- Differential Diagnosis – Cystic Corpus Luteum
Homogeneous and regular hypoechoic image.
Persistence over 2 follow-up ultrasounds over a period of 9 months : misdiagnosis of endometrioma.
No MRI.
Pathology : cystic corpus luteum.
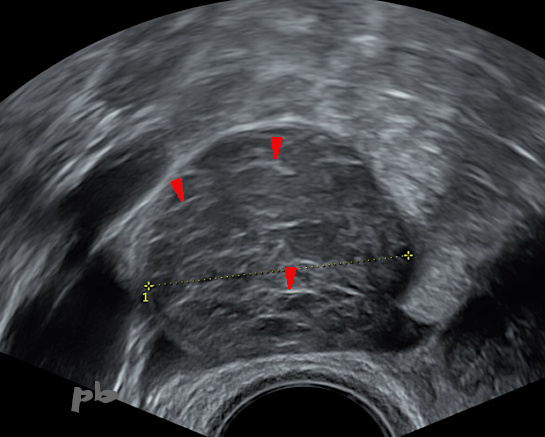
15 – Diagnostic différentiel – Kyste hémorragique fonctionnel
Patiente se présentant pour des métrorragies et des douleur pelviennes droites.
Echographie du 29/7 : suspicion d’adénomyose et kyste ovarien droit fonctionnel hémorragique typique. Fines travées hyperéchogènes internes (►).
15 – Differential Diagnosis – Functional Hemorrhagic Cyst
Patient presenting with metrorrhagia and right pelvic pain.
Ultrasound from 29/7 : suspicion of adenomyosis and typical right functional hemorrhagic ovarian cyst. Fine internal hyperechoic streaks (►).
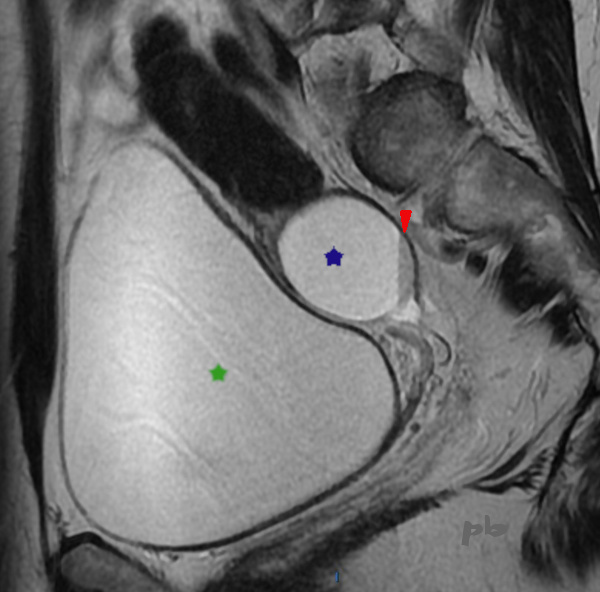
16 – Diagnostic différentiel – Kyste hémorragique fonctionnel
(même patiente que 15)
IRM le 17/8 pour confirmation de l’adénomyose (et non pour le kyste ovarien, typique d’une origine fonctionnelle en écho) : le kyste (★) présente un sédiment hématique en signal T2 intermédiaire (►) et hypersignal T1 (non montré).
Vessie pleine (★).
Echo le 15/11 : disparition du kyste, confirmant son origine fonctionnelle.
16 – Differential Diagnosis – Functional Hemorrhagic Cyst
(same patient as 15)
MRI on 17/8 to confirm adenomyosis (and not for the ovarian cyst, typical of a functional origin on ultrasound) : the cyst (★) presents a hematologic sediment in intermediate T2 signal (►) and T1 hypersignal (not shown).
Full bladder (★)
Ultrasound on 15/11 : disappearance of the cyst, confirming its functional origin.
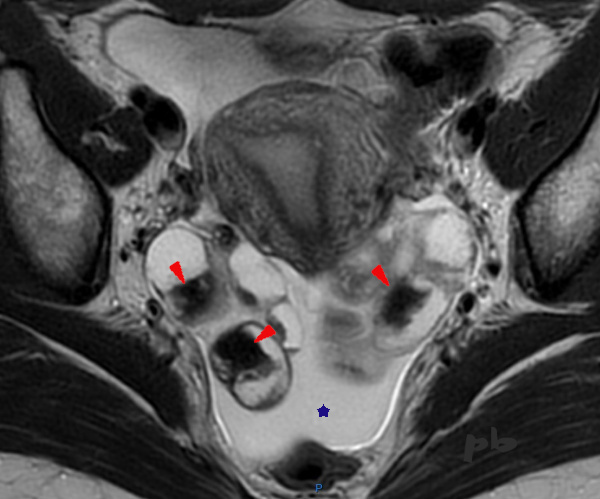
17 – Diagnostic différentiel IRM – Saignement intra-folliculaire
IRM coupe axiale T2.
L’IRM est réalisée dans le cadre d’un bilan d’endométriose profonde.
Mise en évidence de multiples images liquidiennes ovariennes bilatérales, en hypersignal, dans lesquelles on retrouve des zones irrégulières en franc hyposignal, de type « shading » (►).
L’interrogatoire permet d’apprendre que la patiente vient de bénéficier d’une stimulation ovarienne en vue d’une FIV, avec ponction folliculaire le matin même de l’examen, expliquant l’ensemble des images.
Le sang récent est en franc hyposignal T2.
Par ailleurs, épanchement dans le Douglas (★).
17 – Differential Diagnosis on MRI – Intrafollicular Hemorrhage Axial T2-weighted MRI image.
The MRI was performed as part of an assessment for deep endometriosis. It reveals multiple bilateral ovarian cystic lesions, appearing hyperintense, within which irregular areas of marked hypointensity, consistent with « shading » (►), are observed. Upon questioning, it was learned that the patient had recently undergone ovarian stimulation for IVF, with follicular puncture performed the same morning as the exam, accounting for these findings. Fresh blood appears markedly hypointense on T2-weighted imaging. Additionally, there is fluid in the pouch of Douglas (★).

18 – Diagnostic différentiel IRM – Saignement intra-folliculaire
(Même patiente que 17)
IRM coupe axiale T1.
Hypersignaux T1 intra-folliculaires (►) : sang.
18 – Differential Diagnosis on MRI – Intrafollicular Hemorrhage
(Same patient as 17)
Axial T1-weighted MRI image.
Intrafollicular T1 hyperintensities (►): blood.
19+20+21- Kystes endométriosique et dermoïde – IRM
Sémiologie IRM comparative entre un kyste endométriosique (►) et un kyste dermoïde (►), tous les 2 ovariens droits.
Ovaire gauche porteur d’un follicule dominant (★).
19+20+21 – Endometriotic and Dermoid Cysts – MRI
Comparative MRI features between an endometriotic cyst (►) and a dermoid cyst (►), both located in the right ovary. The left ovary contains a dominant follicle (★).
| T2 (image 19) | T1 sans fatsat (image 20) | T1 avec fatsat (image 21) | |
| Endométriome (►) | hypersignal | hypersignal | hypersignal |
| kyste dermoïde (►) | Hypersignal Nodule central hyposignal | Hypersignal Nodule central hyposignal | Hyposignal Nodule central hyposignal |
Le kyste dermoïde, contenant de la graisse, apparait en noir sur la séquence T1 fatsat (qui supprime le signal de la graisse), alors que le signal du sang ne se modifie pas. Les autres tissus contenant de la graisse ((sous-cutanés par exemple) deviennent également noirs.
L’hypersignal en T2 du kyste endométriosique n’est pas très fréquent, ni caractéristique, au contraire du »shading ». L’hypersignal en T1 fatsat permet le diagnostic.
In T1 fat-saturated sequences (which suppress the fat signal), a dermoid cyst (containing fat) appears black, whereas the signal from blood remains unchanged. Other fat-containing tissues (such as subcutaneous fat) also turn black.
A T2 hyperintense signal in an endometriotic cyst is neither very common nor characteristic, unlike « shading ». However, T1 fat-saturated hyperintensity enables the diagnosis.
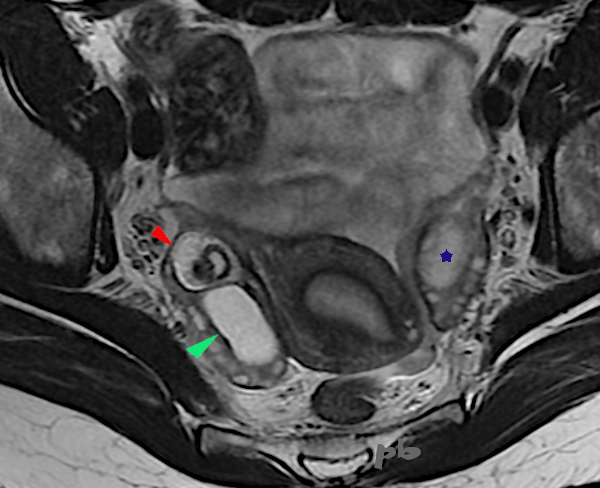
19- T2
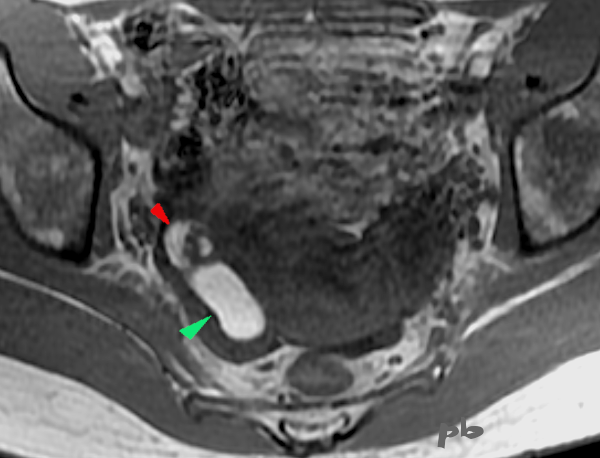
20- T1 sans fatsat
20 – T1 without fatsat
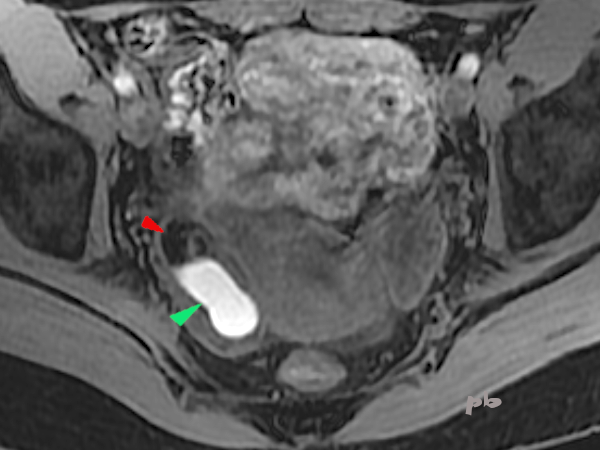
21 – T1 avec fatsat
21 – T1 fatsat
© Dr Philippe BASSNAGEL – 2021
