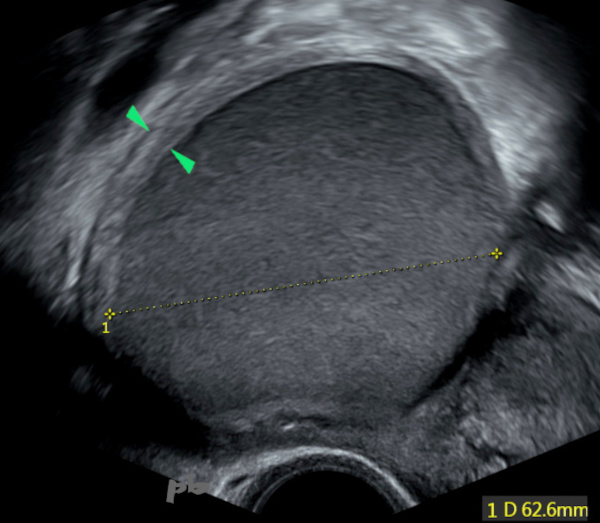
1 – Kyste endométriosique – Echographie
Kyste endométriosique typique en échographie (croix) : contenu échogène, d’échogénicité globalement égale au myomètre, homogène. Contours réguliers.
Pas d’atténuation acoustique.
Coque ovarienne (►) bien visible. Son repérage et l’évaluation folliculaire sont des éléments importants du compte rendu du fait du risque accru d’infertilité chez ces patientes et dans l’éventualité d’une exérèse chirurgicale.
1 – Endometriotic Cyst – Ultrasound
Typical endometriotic cyst on ultrasound (cross) : echogenic content, with overall echogenicity equal to the myometrium, homogeneous. Regular contours.
No acoustic attenuation.
Ovarian shell (►) clearly visible. Its identification and follicular evaluation are important elements of the report due to the increased risk of infertility in these patients and in the event of surgical excision.
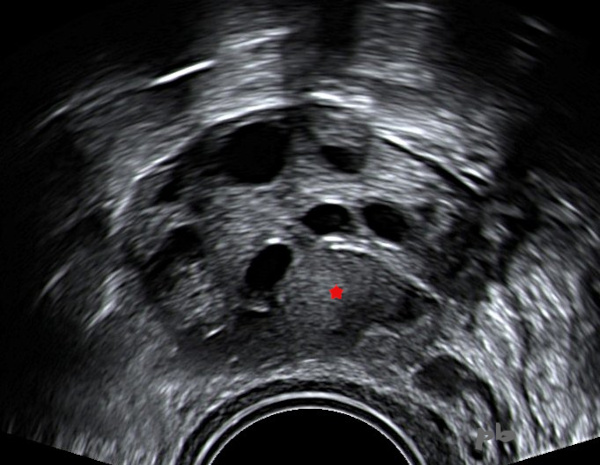
2- Kyste endométriosique – Echographie
Ovaire porteur de plusieurs follicules anéchogènes.
Au milieu, un petit kyste isoéchogène, endométriosique (★).
On note un discret renforcement postérieur en arrière, plutôt en faveur de la nature liquidienne et non solide.
2- Endometriotic Cyst – Ultrasound
Ovary containing several anechoic follicles.
In the middle, a small isoechoic, endometriotic cyst (★).
There is a slight posterior reinforcement behind, more in favor of a liquid rather than solid nature.
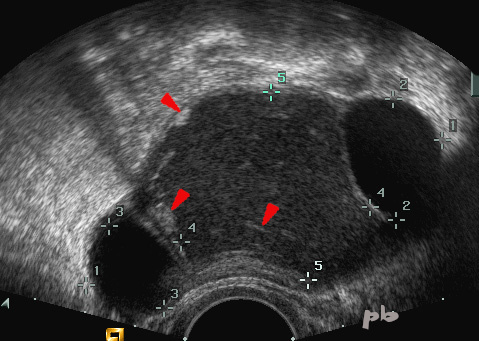
3- Kyste endométriosique – Echo
Présence de 3 kystes : un kyste isoéchogène (entre les croix 4 et 5), et de chaque côté un kyste très hypoéchogène.
Le kyste isoéchogène contient plusieurs images hyperéchogènes (►), déclives ou en suspension. Ces images sont supposées correspondre à des caillots ou des cristaux de cholestérol. Elles sont très évocatrices de l’origine endométriosique.
3- Endometriotic Cyst – Ultrasound
Presence of 3 cysts : one isoechoic cyst (between the crosses 4 and 5), and on each side, a very hypoechoic cyst.
The isoechoic cyst contains several hyperechoic images (►), either dependent or suspended. These images are assumed to correspond to clots or cholesterol crystals. They are highly suggestive of an endometriotic origin.
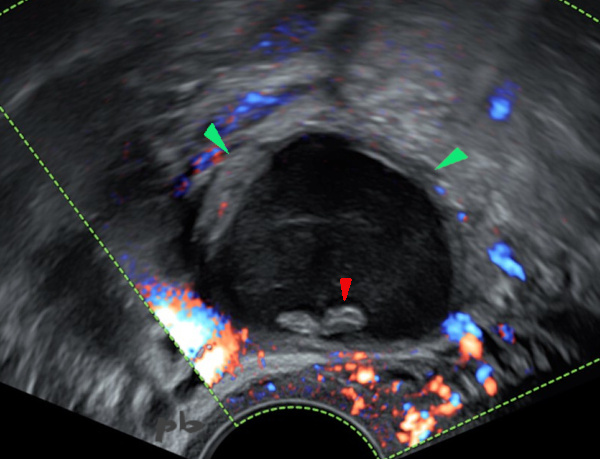
4- Kyste endométriosique – Echodoppler
Kyste endométriosique hypoéchogène.
2 plages déclives hyperéchogènes sans flux en doppler couleur (►) : caillots et/ou dépôts de cholestérol.
Parenchyme ovarien (►) en périphérie avec micro follicules.
4- Endometriotic Cyst – doppler
Hypoechoic endometriotic cyst.
Two dependent hyperechoic areas without flow on color Doppler (►) : clots and/or cholesterol deposits.
Ovarian parenchyma (►) in the periphery with micro follicles.

5- Kyste endométriosique – Echo
Kyste endométriosique avec niveaux.
L’arrière de la patiente étant à gauche sur l’image, le liquide le plus dense ou épais se situe aussi à gauche (★). Le liquide le plus léger ou le moins « dense » ou surnageant est à droite (★).
Cet aspect de niveau n’est pas totalement spécifique d’une origine endométriosique, puisqu’on peut le rencontrer dans les kystes fonctionnels, voire les kystes dermoïdes.
5- Endometriotic Cyst – Ultrasound
Endometriotic cyst with fluid levels.
With the patient’s back on the left side of the image, the densest or thickest fluid is also on the left (★). The lightest or least dense fluid, is on the right (★).
This layered appearance is not entirely specific to an endometriotic origin, as it can also be found in functional cysts or even dermoid cysts.
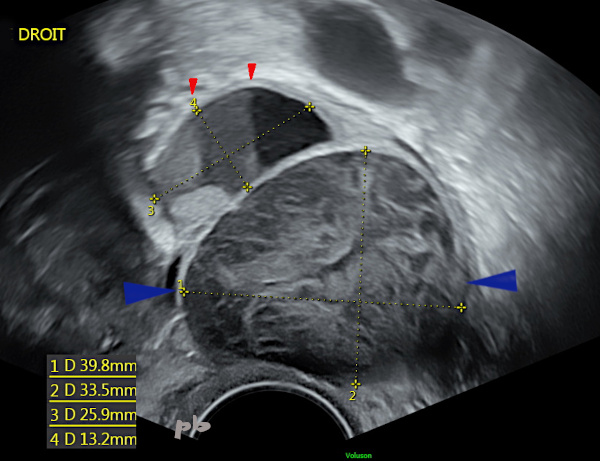
6- Kyste endométriosique / kyste fonctionnel – Echo
Petit kyste endométriosique supérieur (croix 3 et 4) avec niveaux (►).
Kyste inférieur de 40 mm (►), fonctionnel hémorragique. Disparition 2 mois plus tard (et persistance du kyste endométriosique).
6- Endometriotic cyst / functional cyst – Ultrasound
Small upper endometriotic cyst (crosses 3 and 4) with levels (►).
Lower cyst of 40 mm (►), hemorrhagic functional. This one disappeared 2 months later (with persistence of the endometriotic cyst).
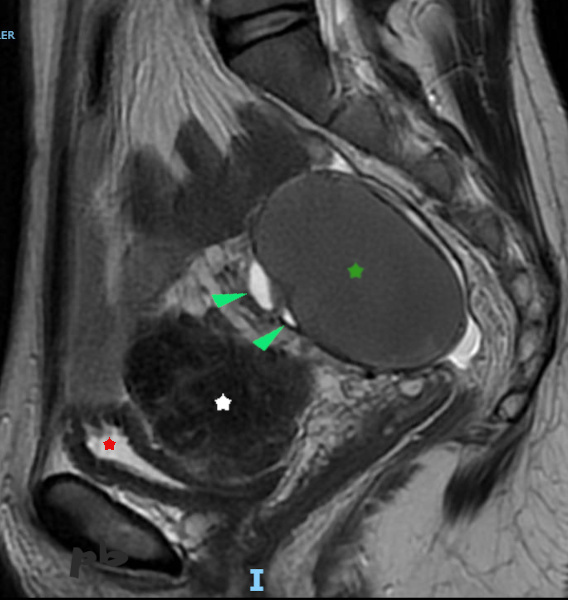
7 – Kyste endométriosique – IRM
Coupe sagittale T2
Kyste endométriosique de signal intermédiaire en pondération T2 (★). C’est un aspect fréquemment rencontré. Les contours sont réguliers. Pas de végétation.
Quelques follicules en hypersignal (►) en avant.
Vessie quasi-vide (★), en hypersignal T2.
Entre l’ovaire et la vessie, fibrome utérin en hyposignal (étoile blanche).
7 – Endometriotic cyst – MRI – Sagittal T2 section
Endometriotic cyst with intermediate signal on T2 weighting (★). This is a frequently encountered appearance. The contours are regular. No vegetation.
A few follicles in hypersignal (►) in front.
Almost empty bladder (★), in T2 hypersignal.
Between the ovary and the bladder, uterine fibroid in hyposignal (white star).
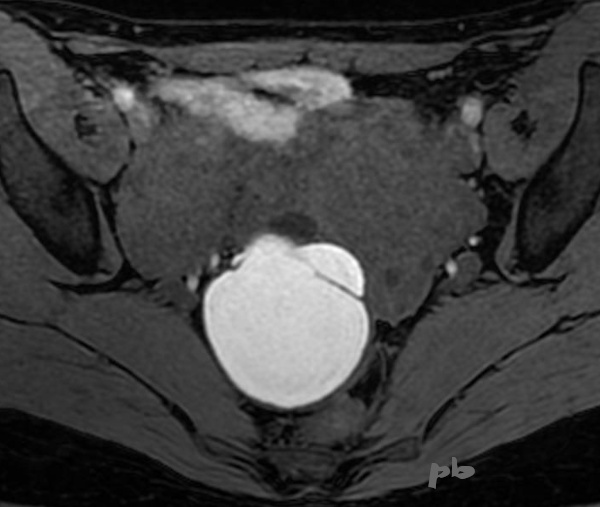
8 – Kyste endométriosique – IRM (même patiente que 7)
Coupe axiale T1 fatsat
Kyste endométriosique en franc hypersignal T1, quasi pathognomonique. Les liquides, en hypersignal sur les séquences en pondération T2, sont hyposignal (« noir ») en T1, sauf le sang.
Attention, les liquides richement protéiques peuvent avoir un signal assez élevé en T1 d’où malgré tout une rare possibilité de diagnostic différentiel.
Pas de nodule tissulaire.
8 – Endometriotic cyst – MRI axial T1 fatsat section
(same patient as 7)
Endometriotic cyst in clear T1 hypersignal, almost pathognomonic. Fluids, in hypersignal on T2-weighted sequences, are hyposignal (« black ») in T1, except for blood.
Note that highly proteinaceous fluids can have a fairly high signal in T1, hence a rare possibility of differential diagnosis.
No tissue nodule.
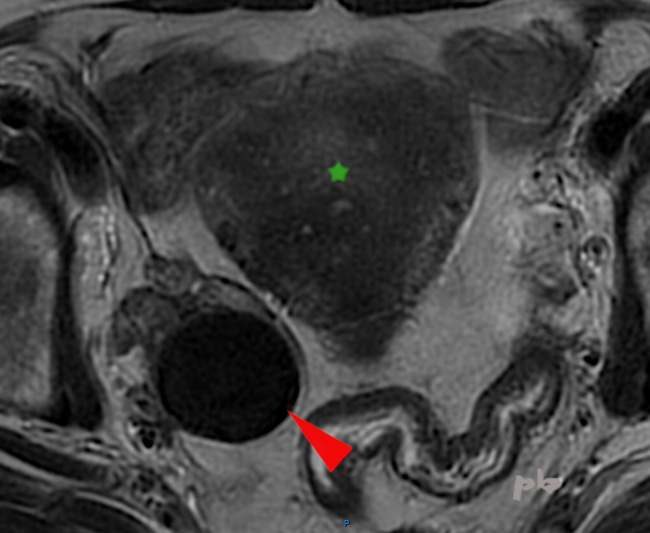
9 – Kyste endométriosique – IRM
Coupe axiale T2.
Un autre aspect de kyste endométriosique en T2 (►) , en franc hyposignal, en anglais « shading » (il avait son hypersignal T1 classique par ailleurs).
Il est considéré comme très spécifique de l’origine endométriosique.
Utérus (★) porteur d’une adénomyose.
9 – Endometriotic cyst – MRI
Axial T2 section.
Another appearance of an endometriotic cyst on T2 (►), in clear hyposignal, or ‘shading’ (it had its classic T1 hypersignal otherwise).
It is considered very specific to endometriotic origin.
Uterus (★) with adenomyosis.

10 – Endométriome – IRM
Coupe sagittale T2
Endométriome avec niveaux (►►) : sédimentation de liquides de densité différente.
Aspect rare et non spécifique (mais peu de diagnostic différentiel : images suivantes).
Hypersignal T1 global par ailleurs.
10 – Endometrioma – MRI
Sagittal T2 section
Endometrioma with levels (►►): sedimentation of fluids of different densities.
Rare and non-specific appearance (but with few differential diagnoses : see following images).
Overall T1 hypersignal otherwise.
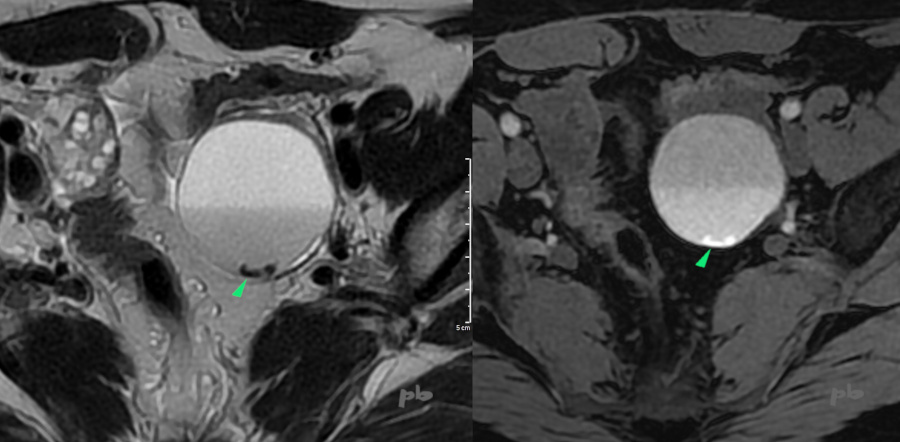
10 bis – Kyste endométriosique – IRM
Coupe axiale T2 (à gauche) et axiale T1 (à droite).
Niveau entre 2 liquides hématiques de densité différente.
Présence de caillots au fond du kyste (►), très hyposignal T2 et hypersignal T1.
10 bis – Endometriotic cyst – MRI
Axial T2 section (left) and axial T1 section (right).
Level between two hemorrhagic fluids of different densities.
Presence of clots at the bottom of the cyst (►), very hyposignal T2 and hypersignal T1.

11- Endométriome – IRM
Coupe sagittale T2
Volumineux kyste ovarien gauche en signal intermédiaire (★). Il atteint 20 cm de grand axe.
Plage hyposignal en déclive, de contours flous (►). Pas de rehaussement après injection.
A ne pas confondre avec une végétation (voir images 24 à 27). Il s’agit de débris cellulaires et/ ou d’amas de cholestérol.
L’anapath a conclu à un kyste endométriosique, sans végétation.
Ovaire droit (★).
11- Endometrioma – MRI – Sagittal T2 section
Large left ovarian cyst with intermediate signal (★). It measures up to 20 cm in its greatest dimension.
Hyposignal area in the dependent portion, with blurred contours (►). No enhancement after injection.
Not to be confused with a vegetation (see images 24 to 27). These are cellular debris and/or cholesterol clumps.
Pathology concluded it was an endometriotic cyst, without vegetation.
Right ovary (★)
© Dr Philippe BASSNAGEL – 2021
